[LUM#1] Very patient robots
How can healthcare professionals be given the opportunity to gain initial experience? At the Faculty of Medicine in Nîmes, caregivers learn or perfect the skills of their profession without putting their patients at risk.
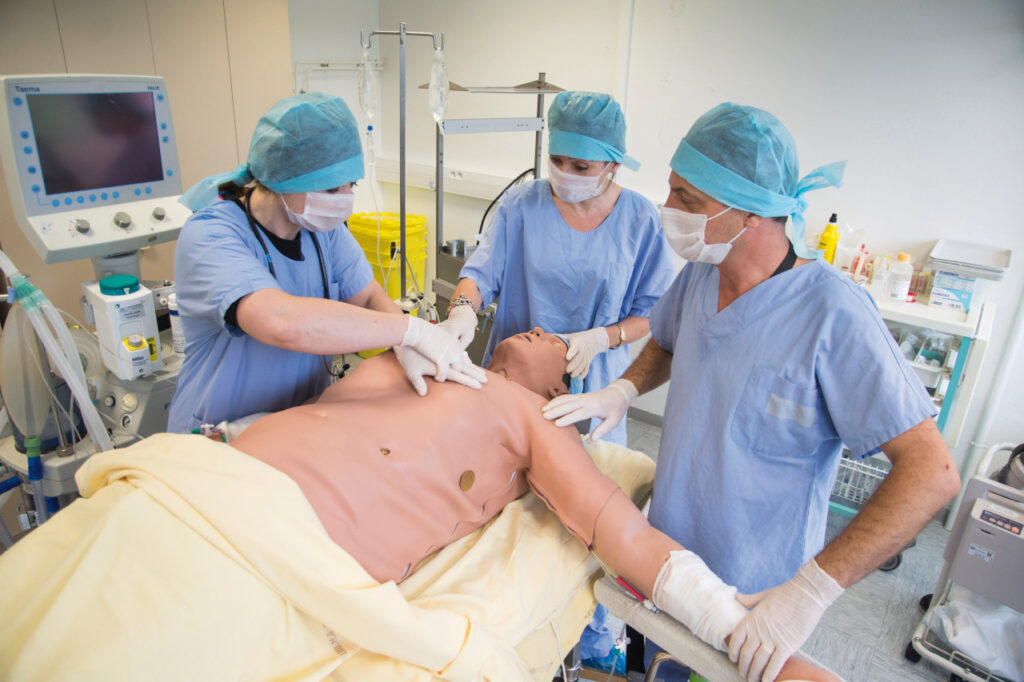
"She's in a lot of pain, doctor. This isn't normal. Do something." The tension is palpable in the delivery room where Noëlle is about to have her fourth child. After three easy births, she has chosen to give birth without an epidural. "Doctor, what's going on? It's taking a long time, isn't it? Is there a problem?" " The father's stress levels are rising. The baby's head is already out, but its body is stuck. Diagnosis: shoulder dystocia. This is an emergency situation that requires immediate action from the medical team. The intern, midwife, and nursing assistant bustling around Noëlle have only a few minutes to deliver the baby.
Emergency situations
Two floors below, Istan, a 30-year-old man, is about to undergo surgery for appendicitis. It's a routine operation. The anesthetists put him to sleep before leaving him in the hands of the surgeons, as usual. But suddenly, the monitoring screen goes haywire: the amount of CO2 exhaled by the young man increases abnormally and his temperature skyrockets. Istan is suffering from malignant hyperthermia, a rare and potentially fatal reaction to anesthesia. To save Istan, the anesthesiologists must administer the appropriate treatment as quickly as possible...
A typical day in a hospital? Not quite. We're not in a hospital. And Noëlle and Istan aren't patients like any others. They're... robots. Welcome to the simulation platform at the Faculty of Medicine in Nîmes. Known as SimHU Nîmes (Simulation Médicale Hospitalo-Universitaire), this exceptional facility allows medical students and other healthcare professionals to train in delicate medical procedures without any risk.
"It also allows working professionals to stay at the top of their game by confronting them with exceptional situations," emphasizes Professor Michel Prudhomme, coordinator of the simulation platform. "These simulation sessions teach them not only how to improve their technical skills, but above all their interpersonal skills," says the project's initiator. Managing a crisis situation, controlling stress and emotions, and knowing how to organize effectively as a team are all skills that are just as vital as medical procedures.
Hyperrealistic simulation
"Simulations force doctors to question themselves and their professional practices," confirms Dr. Lana Zoric, scientific director of anesthesia simulations. She programmed the malignant hyperthermia in "Istan." "We prepare the scenarios in advance and develop them in real time, which is very stressful for anesthesiologists."It was also very stressful for the team that took care of "Noëlle." In the delivery room, the intern, midwife, and nursing assistant almost forgot that their patient was not quite like the others. "We experience it as a real delivery," says Marie-Pascale Villette. The young midwife has already performed deliveries but has never had to deal with shoulder dystocia. "At least now I know what to expect and I'll react better in a real situation. This simulation allows me to be a better midwife."By doing the right things but also by optimizing teamwork."Each simulation session is followed by a debriefing where we discuss what was done and what could have been improved, an essential opportunity for reflection and discussion ," explains Valérie Courtin, educational and scientific manager of the midwifery platform.
A guarantee of safety for patients
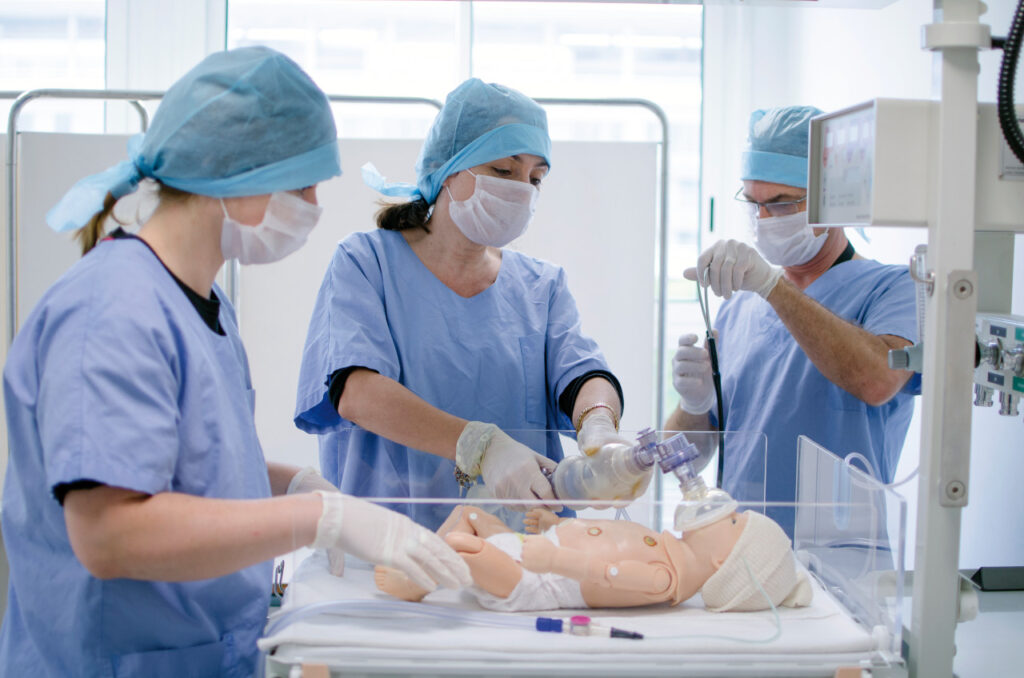
In addition to Noëlle and Istan, the Faculty of Medicine in Nîmes also has a newborn robot. These mannequins have already been used by dozens of midwives, pediatric nurses, nursing assistants, pediatricians, emergency physicians, and anesthesiologists. And that's not all: "the simulation platform also has an anatomy laboratory where surgeons, radiologists, and physical therapists can refine their techniques." There are no high-techrobots here: students and doctors train on human bodies donated to science. They can also perform operations on pig models, as pigs are the animals whose physiology most closely resembles that of humans. "This platform is one of the most comprehensive in France, " says Michel Prudhomme. "All of these simulation tools enable doctors to maintain their excellent standards, but also to train in innovative techniques without any risk to patients."
Noëlle's delivery is over. Everything went well, and the relieved medical team proudly holds up a healthy robot baby. Istan, meanwhile, was saved thanks to the composure and quick reactions of the anesthetists. That's certainly reassuring.
Find UM podcasts now available on your favorite platform (Spotify, Deezer, Apple Podcasts, Amazon Music, etc.).