Digital health: UM "sets the standard" with ESNbyUM
A pioneer in medicine for eight centuries, the University intends to remain so in the digital age with the creation of ESNbyUM. A digital health school that will train future healthcare professionals, as well as lawyers, engineers, and administrators, starting in 2023. This project is supported by the government as part of the "Skills and Jobs of the Future" call for expressions of interest and will serve as the foundation for the region's future center of excellence in digital health.
"For the past decade, digital technology has been revolutionizing the healthcare profession and has become part of everyday life for professionals who use software, electronic patient records, or who are confronted with issues of identity vigilance, cybersecurity, or telemedicine," explains Maurice Hayot, professor at the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Montpellier and hospital practitioner at the University Hospital Center. However, at present, there is no specific training dedicated to these issues, with all the problems that this can pose in terms of security, confidentiality, etc. "
Highest national funding
To address this shortfall, UM asked Maurice Hayot, supported by a project team of experts in the field, to respond to the call for expressions of interest (AMI) entitled "Skills and professions of the future" launched by the government as part of the Future Investment Program 4 (France 2030). " To develop our project, we brought together professors, researchers, trainers, and companies with the aim of building a digital health school that truly reflects professional expertise," explains Maurice Hayot. It was a winning bet, as the Montpellier project was not only one of 66 winners selected by the government this summer, but also received the largest amount of funding in the "digital health training programs" category, pocketing the tidy sum of €4 million.
The Region, which wishes to make this project the foundation of its future center of excellence in digital health, will contribute €600,000. These substantial sums are in addition to the resources allocated by the consortium members, foremost among which are, of course, the University of Montpellier and the Montpellier and Nîmes University Hospitals, but also training organizations and private companies (see box). In total, the Digital Health School will have a budget of nearly €8 million.
Five out of five
"The call for tenders proposed targeting at least one audience among the five proposed. We chose to target all five, firstly because we have a history of training in this field in Montpellier, and secondly because we want to lay the foundations for a center of excellence in digital health training that will become a national benchmark. This naturally includes future healthcare professionals, whether they are students of medicine, pharmacy, dentistry, midwifery, or healthcare or nursing training institutes, or whether they are destined for paramedical professions such as physiotherapist or occupational therapist, or even professionals in adapted physical activity from STAPS (Science and Technical Studies in Physical Activity and Sports).
Next come digital specialists (engineering sciences, technology specialists, etc.), managers of health and social care organizations, and lawyers, because "we need specialists in digital health law to support and protect patients, professionals, and institutions that use digital health," explains Maurice Hayot. Finally, there are expert professionals capable of certifying digital medical devices , "something France sorely lacks in order to become an international leader," he adds.
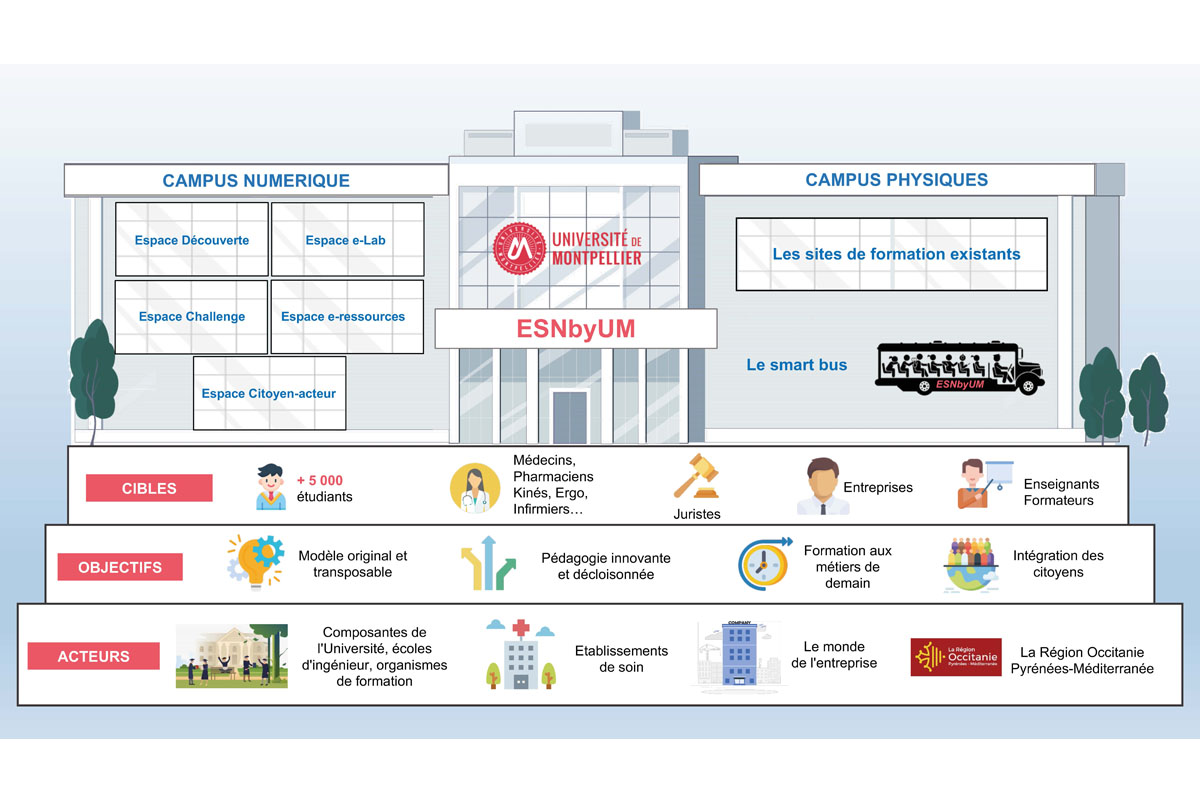
Named ESNbyUM for "École de santé numérique de l'Université de Montpellier" (Montpellier University Digital Health School), this school "should not be taken as a school in the strict sense of the term, but rather in the sense of 'setting an example' by passing on generic or specific skills to each audience, some of which constitute a core knowledge framework defined by the Ministry of Health, through the Ministerial Delegation for Digital Health," continues Maurice Hayot. In concrete terms, for undergraduate health students, this will involve blocks of skills integrated into current courses for widespread implementation from the start of the 2023 academic year. These will cover health data, cybersecurity, digital tools in health, telehealth, and health communication. For graduate and postgraduate students, or for professionals enrolled in continuing education, customized modules closely aligned with their professional practices and specialties will be offered during the year.
A 6P Teaching Methodology
"Personalized" is one of the key words in the teaching approach designed and developed for this training program by Maurice Hayot's team. "Our goal with ESNbyUM is to create an innovative and effective teaching model for training professionals who will practice humanistic digital health, and to ensure that this model can be replicated in other cities. We want to develop and deploy a 'precision teaching method' where everyone can acquire the skills they specifically need for their practice, depending on their initial background, availability, or geographical location within the region," insists the professor. This method, known as '6P Teaching', is based on six pillars: Personalized; Preventive,"i.e., preventing people from abandoning the practice due to insufficient training"; Predictive,"capable of predicting the needs and therefore the jobs of tomorrow in digital health"; Participatory,"empowering learners to take control of their learning choices and career paths"; Evidence-based and Practice-centered.
More specifically, this school will be based on the creation of a digital campus where students and professionals in training will have access to various spaces: discovery of digital health terminology, challenges between students/learners, an e-lab linked to the business world, resources for becoming a trainer yourself, and exchanges with and between citizens. "This innovative space was designed in collaboration with the Institute of Business Administration (IAE) to enable people from different professions or specialties to work together on the same project. In the digital age, healthcare professionals can no longer remain isolated; they must interact with engineers, lawyers,and others," says Maurice Hayot. Funded for a period of five years, ESNbyUM aims to become the new French model for training in emerging healthcare professions.
They are part of the ESNbyUM consortium:
The consortium members include, of course, the University of Montpellier, with most of its departments, the Montpellier and Nîmes university hospitals, as well as: the Montpellier Regional Cancer Institute, the engineering schools Polytech Montpellier, IMT Mines Alès, and ISIS Castres, GRADeS e-santé Occitanie (Regional Support Group for the Development of e-Health), training organizations such as FORMATICSanté, the KEEFP association, which brings together training institutes for occupational therapists and physiotherapists (IFMK, IFE, EPK), the GCS IFSI group (nursing training institute) and KORIAN Academy, the Korian group's internal training organization, as well as companies such as ONAOS and the Pfizer Innovation endowment fund.
They support ESNbyUM: