Biology and Health Division
Five research clusters (Agriculture, Environment, Biodiversity; Biology-Health; Chemistry; Mathematics, Computer Science, Physics, Systems; Social Sciences) were created in September 2019 within the MUSE Foundation, then established as intermediate structures of the University of Montpellier when it was created as an experimental public institution in 2022.
The Biology-Health research cluster is a hub for scientific activity, bringing together research structures and stakeholders and providing a forum for scientific consultation with a view to developing joint initiatives between the partners represented on the Strategic and Structural Investment Committee (COMIS).
Governance of the cluster
Director of the Biology-Health Division: Pierre-Emmanuel Milhiet
Administration and Management Support Officer: Laure Bourbon
Head of the Human Resources Committee (CRH) and Deputy Director: Jean-Yves Le Guennec
Human Resources Committee (CRH) Manager: Magali Fayol-Chastaing
Strategic Steering Committee (SSC)
The Strategic Steering Committee acts as a link between the Research Cluster Research institutional partners. It helps define the Research Cluster's major scientific strategic orientations Research gives its opinion on the action plan proposed by the Director of the Research Cluster.
Pole Council
The Cluster Council provides advisory opinions on the direction and implementation of the Cluster's actions and strategy.
Executive Board
It includes members of the division's management team, one BIATS representative, one doctoral student representative, representatives from the research areas, and representatives from the working groups.
Human Resources Committee (HRC)
The Human Resources Committee deals with issues specific to the staff of the University of Montpellier. Each Human Resources Committee issues an advisory opinion, in accordance with the statutory provisions specific to Professors researchers.
Key figures
24 Biology and Health Laboratories
8 Partner Institutions
4 Research SupportUnit
3 Technology Platforms
7 ResearchThemes
2 DoctoralSchools (CBS2: Chemical and Biological Sciences for Health, SMH: Human Movement Sciences)
1 LabUM EpiGenMed
106 other PIA (Equipex, etc.)
2 Centers of Excellence: CoEN & CeAND
1 SIRIC ( Research Cancer Research Site)
5 FHUs (University Hospital Federations)
6 Nationalinfrastructures
44 Start-ups
8 ERC (European Research Council)
1 IUF (Institut Universitaire de France)
975 teachers and researchers
1,581 doctoral students / 7,088 doctoral students at UM
5,062publications
413 theses defended
233 industrial and R&Dcontracts
111 patents
41 CIFREscholarships
over the period 2020-2025:
3 ATIP/AVENIR teams
Partner institutions
- CIRAD – Center for International Cooperation in Research for Development
- Montpellier University Hospital – Montpellier University Hospital Center
- CHU Nîmes – Nîmes University Hospital Center
- CNRS – National Center for Research
- ICM – Montpellier Cancer Institute
- INRAE – National Research Institute Research Agriculture, Food, and the Environment
- INSERM – National Institute of Health and Research
- IRD – Research Institute Research Development
Responsibilities of the division
The Biology-Health Research Cluster is responsible for:
- set up scientific activities within the community on specific themes or topics and develop scientific prospects;
- initiate and coordinate responses to calls for cross-cutting regional, national, or international projects;
- participate in the deployment of the University of Montpellier's international strategy and visibility;
- propose concerted actions to promote the link between Training and Research
- participate in forward planning for jobs and skills;
- Establish a Human Resources Committee and ensure its proper functioning in order to produce opinions on specific issues relating to human resources in research at the University of Montpellier.
Scientific scope
- Partner institutions of the University of Montpellier involved in the Research Cluster.
- Research structures affiliated with the Research Cluster.
- Support and Research Units Research SRUs).
- Technology platforms.
- Doctoral schools: CBS2 (Chemical and Biological Sciences for Health) & SMH (Human Movement Sciences).
- The Training and Research Units Research UFR), schools, and institutes of the University of Montpellier linked to the Research Cluster
Research areas
The Biology-Health Research Cluster is organized into seven thematic areas of research, teaching, and outreach.
Each area is represented by an Professor representative (plus a substitute), an appointed unit director representative, and an appointed university hospital representative.
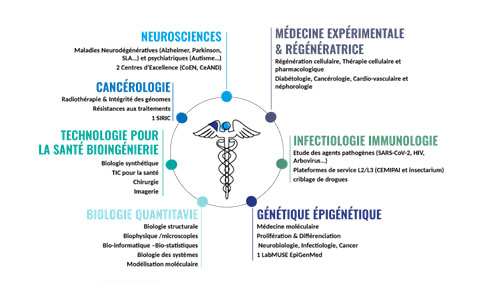
Quantitative Biology
ResearchProfessor: Chérine Béchara (IGF)
+ substitute: Antoine Le Gall (CBS)
DU representative: Pierre-Emmanuel Milhiet (CBS)
HU representative: Nicolas Molinari (IDESP)
Quantitative biology aims to understand the underlying principles of complex biological behaviors in terms of physical and mathematical parameters. It is therefore an approach that concerns all fields of biology and relies on technological expertise such as:
- Structural biology
- Biophysics and microscopy, from single molecules to tissue
- Bioinformatics (structural, genomic, etc.) and biostatistics
- Systems biology
- Multiscale molecular modeling
This community brings together 40 research teams spread across nine research units (CBS, CRBM, IGF, IGH, IGMM, IRIM, IRCM, LBN, LPHI).
The Quantitative Biology community, whose teams are supported by prestigious funding (ERC, ATIP-Avenir, Bettencourt-Schueller, etc.), coordinates and/or participates in several projects labeled "Investment Program for the Future": the Integrative Structural Bioinformatics (Bip-Bip) project and three national infrastructures in the fields of optical imaging (France Bio-Imaging-FBI), structural biology (French Integrated Structural Biology Infrastructure – FRISBI), and chemoinformatics (ChemBioFrance). In addition, several teams working in this field are key players in prestigious international networks (Physics of Living Systems, LifeTime).
Oncology
ResearchProfessor: Jacques Colinge (IRCM)
+ substitute: Céline Gongora (IRCM)
DU representative: Nathalie Bonnefoy (IRCM)
HU representative: Guillaume Cartron (IGMM)
Montpellier's large cancer research community is involved in understanding the fundamental mechanisms of cancer and improving its treatment.
It brings together around fifty teams spread across ten joint research units under the supervision of the University of Montpellier and the CNRS or Inserm (CBS, CRBM, IGF, IGH, IGMM, IRCM, IRIM, IRMB, LPHI, PhyMedExp) as well as three healthcare centers (Montpellier University Hospital, Nîmes University Hospital, and ICM).
This community's excellence in research is internationally recognized. This is reflected in national certifications:
- The "SIRIC Montpellier Cancer" project was certified in 2013, 2018, and then 2023 by INCa, DGOS, and AVIESAN.
SIRIC Montpellier Cancer is one of eight Research Cancer Research Centers in France. Based on the American Comprehensive Cancer Centers model, it brings together clinicians and researchers from the Montpellier Cancer Institute, Montpellier University Hospital, and eight research institutes affiliated with Inserm, CNRS, and the two universities of Montpellier on a single site. Drawing on multidisciplinary research teams (clinical, biology, physics, mathematics, humanities, and social sciences) and cutting-edge technology platforms, SIRIC Montpellier Cancer is currently conducting integrated and innovative research on three central themes—radiotherapy, prevention and supportive care, and onco-metabolism—with the ultimate goal of transforming clinical practices in oncology. - EvoCan University Hospital Federation (FHU) project certified in 2017 and 2023 by AVIESAN
Complementing and coordinating with SIRIC, EvoCan has been dedicated since 2023 to the development and clinical deployment of immunotherapies, which represent a major avenue for fighting tumors. This includes both antibodies targeting molecules that modulate the immune system and immunocellular approaches using genetically modified T cells (CAR-T cells). - Several cancer teams in Montpellier are certified by the National League Against Cancer (Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer) and the Foundation for Research (Fondation pour la Research , FRM), or are part of the LabEx "MabImprove" or LabMUSE "EpiGenMed" at the Montpellier I-Site MUSE.
Genetics-Epigenetics
ResearchProfessor: Robert Feil (IGMM)
+ substitute: Rosemary Kiernan (IGH)
DU representative: Philippe Pasero (IGH)
HU representative: David Genevieve (IRMB)
The Montpellier Genetics-Epigenetics Community represents 22 teams spread across 14 research units (CBS, CRBM, DEFE, DMEM, IGF, IGH, IGMM, INM, Intertryp, IRCM, IRIM, IRMB, LPHI, PhyMedExp).
In 2010, as part of the Investing in the Future Program, the excellence of research in this field was recognized with the creation of the EpiGenMed Laboratory of Excellence. LabEx EpiGenMed has been remarkably successful, with major discoveries made by its teams being rewarded with national and international prizes and distinctions. EpiGenMed has been designated a Montpellier University Laboratory of Excellence (LabMUSE) as part of the I-SITE project. Its objective is to promote fundamental and clinical research by setting up interdisciplinary projects "to move from the genome and epigenome to the molecular medicine of tomorrow." The research teams of excellence study the implications of genetics and epigenetics in cell proliferation and differentiation, normal development, neurobiology, infectious diseases, and cancer, in close collaboration with the Montpellier research community.
This area of research also targets clinical applications in several fields. To this end, in 2018 Montpellier University Hospital entered into a partnership to promote the translation of discoveries from basic scientific research into medical research applications. Within this framework, the clinical teams of the Montpellier-Nîmes inter-hospital federation of medical genetics and molecular medicine (3 clinical units, 15 hospital laboratories) joined the existing teams of the Genetics-Epigenetics research area. This scientific integration aims to develop partnerships that will combine scientific discoveries in genetics and epigenetics with future medical applications.
Infectious Diseases and Immunology
ResearchProfessor: Nathalie Chazal (IRIM)
+ substitute: Jean-Philippe Lavigne (VBIC)
DU representative: Matteo Bonazzi (IRIM)
HU representative: Edouard Tuaillon (PCCEI)
The Infectious Diseases and Immunology community is organized as a continuum of Research , Research , and population Research . It includes a University Hospital Federation (FHU) called "Infection and Chronicity" (InCh) and brings together seven hospital departments from the Montpellier and Nîmes University Hospitals, 17 research units (ASTRE, CBS, CRBM, IGF, IGH, IGMM, IMAGINE, Intertryp, IRCM, IRIM, IRMB, LPHI, MIVEGEC, PCCEI, TransVIHMI, VBIC), and a hospital platform (LECRII).
This community, which has a major international influence with several laboratories established abroad (Africa, Asia, South America in cooperation with IRD and CIRAD organizations), is heavily involved in numerous international projects focusing on viral infections (HIV, Ebola, SARS-CoV-2, Arbovirus, HTLV-1, Influenza), parasitic (Plasmodium, Toxoplasma), bacterial (Mycobacterium, Coxellia, Brucella, Pseudomanas, Staphylococcus, antibiotic resistance and multi-resistance) and neglected tropical diseases (trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis).
In addition to these projects, the exceptional technical facilities of the UAR BioCampus Montpellier, which benefit all researchers in Biology and Health, this community also benefits from other more specific technical platforms such as those of the UAR CEMIPAI (Center for the Study of Infectious Diseases and Anti-Infectious Pharmacology) and the infrastructure for housing, breeding, experimental conditioning, and experimentation in the A2/A3 animal facilities and the I2/I3 Insectarium.
Finally, an important partnership has been developed with large industrial groups and well-established SMEs/VSEs, including Horiba, SANOFI-Aventis, Biorad, Abivax, Metafora, Deinove, Nosopharm, and Azilead.
Experimental and Regenerative Medicine
ResearchProfessor: Jean-Marc Brondello (IRMB)
+ substitute: Delphine Gitenay (IRMB)
DU representative: Alain Lacampagne (PhyMedExp)
HU representative: Christian Jorgensen (IRMB)
Experimental and Regenerative Medicine is the study of the mechanistic basis of diseases and the development of new therapies based on tissue regeneration, cell therapy, and pharmacology. With this objective in mind, the teams working in this area have developed unique models of target human diseases, as well as patient cohorts, enabling them to test innovative therapies.
This community comprises 27 teams spread across nine research units (BC2M, DMEM, EuromovDMH, IGF, IGH, INM, IRMB, MMDN, PhyMedExp).
The excellence of this community is recognized by the certification of a National Infrastructure in Biology and Health: E-Cell France, which offers services covering all phases of a cell therapy project, and by the AVIESAN certification of the RegenHab University Hospital Federation (FHU).
The RegenHab FHU is a clinical, biological, and technological consortium that brings together stem cell biologists, physiologists, robotics engineers, specialists in complex movement imaging, and clinicians in rheumatology, muscular diseases, anesthesia-resuscitation, and rehabilitation. It develops new therapeutic approaches to restore movement in patients with diseases that impair musculoskeletal tissue function.
Neuroscience
ResearchProfessor: Sylvie Claeysen (IGF)
+ substitute: Fabrice Ango (INM)
DU representative: Sylvain Lehmann (INM)
HU representative: Philippe Marin (IGF)
The Montpellier Neuroscience Community brings together researchers, teacher-researchers, and clinicians working at the university hospitals of Nîmes and Montpellier and 30 teams spread across six research units (CRBM, IGF, IGH, IGMM, INM, MMDN).
It has two Centers of Excellence. The first, the Montpellier Center of Excellence for Neurodegenerative Diseases (CoEN), certified by AVIESAN, focuses specifically on biomarkers and personalized medicine. The center aims to promote multidisciplinary projects combining fundamental, preclinical, clinical, epidemiological, and social science research on diseases that are major public health challenges, such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, multiple sclerosis, and ALS.
The second is the Center of Excellence on Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disorders "CeAND," an interdisciplinary research and education network aimed at promoting interaction between researchers, professionals in the field, and affected individuals, with the objectives of identifying the determinants of autism spectrum disorder/neurodevelopmental disorders, developing biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis, and enabling personalized medicine. In addition, CeAND has been certified by the Interministerial Delegation for the National Strategy on Autism within Neurodevelopmental Disorders.
The Neuroscience Community also has a University Hospital Federation (FHU NEUROCLIN), whose aim is to structure neuroscience research in areas where there is strong regional expertise (sensory-motor disorders, neurodegeneration, cognition, psychiatry), through to clinical trials and the creation of companies to develop new drugs or technological devices.
These centers of excellence work in close synergy, particularly in the area of biomarkers, sharing multicenter cohorts, certified biobanks, and cutting-edge technological approaches (NGS, quantitative mass spectrometry, multiplex and ultrasensitive immuno-detection, etc.).
Health Technology – Bioengineering
ResearchProfessor: Denis Mottet (EuroMov)
+ substitute: Prisca Boisguérin (PhyMedExp)
DU representative: Stéphane Perrey (EuroMov)
HU representative: Maurice Hayot (PhyMedExp)
This area covers four main themes ranging from synthetic biology to information and communication technologies (ICT) for health, surgery, and imaging.
Bioengineering encompasses all in vitro diagnostic and/or analytical technologies, their implementation in living organisms, and biomaterial aspects.
Synthetic biology is a recent discipline that combines biology and engineering to design new living biological systems for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. The teams involved in this field are the clinical teams at Montpellier University Hospital (endocrinology, diabetes, psychiatric emergencies and post-emergencies, wounds and healing) and 31 fundamental research teams spread across 16 research units (BC2M, CBS, EuromovDMH, IGF, IGH, IGMM, INM, IRCM, IRIM, IRMB, LBN, Li2D, MMDN, PhyMedExp, Sys2Diag, TransVIHMI).
ICTs are increasingly used in patients with chronic diseases and the elderly. They enable the collection and monitoring of biomarkers necessary for patient care, treatment adjustment, and rehabilitation. The main teams involved in this field are departments at Montpellier University Hospital (Nutrition Department, Clinical Physiology Department) and
research teams such as: PhyMedExp, LBN, Epsylon, EA MRM, and the Institut des Mines d'Alès. Beyond clinical services and research laboratories, these activities are also carried out within two FHUs (ICT4CARE and REGENHAB).
An e-Health chair has been developed in this field within the Entreprendre Foundation at the University of Montpellier.
The theme of "Surgery" covers not only surgical technologies, including remote surgery, materials, and related equipment, but also implantable devices, functional replacement devices, and prostheses.
The Imaging theme includes all anatomical and functional imaging technologies, both in vitro and in vivo.
Research structures
- Montpellier BioCampus (BCM)
- Biocommunication in Cardio-Metabolic (BC2M)
- Lunaret BioCenter Montpellier (BIOLuM)
- Stem cells, cellular plasticity, tissue regeneration, and immunotherapy for inflammatory diseases (IRMB)
- Center for Infectious Disease Studies and Anti-Infective Pharmacology (CEMIPAI)
- Center for Structural Biology (CBS)
- Montpellier Cell Research Center (CRBM)
- Embryonic Development, Fertility, and Environment (EDFE)
- Muscle dynamics and metabolism (MDM)
- EuroMov Digital Health in Motion (EuroMov DHM)
- Genopolis
- Initial Management and Prevention of Acute Organ Failures in Critically Ill Patients (IMAGINE)
- Institute of Human Genetics (IGH)
- Montpellier Institute of Molecular Genetics (IGMM)
- Institute of Functional Genomics (IGF)
- Montpellier Institute of Neuroscience (INM)
- Montpellier Research Institute (IRCM)
- Montpellier Infectious Research Institute (IRIM)
- Desbrest Institute of Epidemiology and Public Health (IDESP)
- Host-Vector-Parasite Interactions in the Environment in Neglected Tropical Diseases Caused by Trypanosomatids (INTERTRYP)
- Bioengineering and Nanosciences Laboratory (LBN)
- Laboratory of Pathogens and Host Immunity (LPHI)
- Molecular Mechanisms in Neurodegenerative Dementias (MMDN)
- Pathogenesis and Control of Chronic and Emerging Infections (PCCEI)
- Physiology and Experimental Medicine of the Heart and Muscles (PhyMedExp)
- Translational Research on HIV and Endemic and Emerging Infectious Diseases (TransVIHMI)
- Bacterial virulence and chronic infections (VBIC)
Partnership research structures:
Technological resources
UAR BIOCAMPUS
BioCampus Montpellier is a Research Support Unit Research UAR 3426 CNRS – US 09 INSERM – UM) for the Biology-Health and Agronomy/Environment/Biodiversity clusters. It brings together 12 high-level technology platforms. The UAR offers its services to research units as well as industrial companies.
- Pharmacology Interactome Screening (Arpege)
- Baculovirus & Therapy (BACFLY)
- Drosophila (DROSO)
- International ImMunoGeneTics information system (IMGT)
- Montpellier Small Animal Imaging (IPAM)
- Montpellier Alliance for Metabolomics & Metabolism Analysis (MAMMA)
- Montpellier DNA Combing (MDC)
- Montpellier Genomic Collections (MGC)
- Montpellier Genomix (MGX)
- Montpellier Imaging Resources (MRI)
- Integrated Platform for Biophysics and Structural Biology (PIBBS)
- Montpellier Organoid Platform (POM)
- Montpellier Proteome Center (PPM)
- Montpellier Vectorology Platform (PVM)
- Montpellier Pet Store Network (RAM)
- Montpellier Experimental Histology Network (RHEM)
- Applied Statistics in Biology (StatABio)
- Zebrafish and Xenopus Platform (ZEFIX)
UAR CEMIPAI – Center for the Study of Infectious Diseases and Anti-Infectious Pharmacology
UAR 3725 CEMIPAI is a service platform under the supervision of the CNRS and the University of Montpellier. It offers in vitro research services on viruses, bacteria, prions, microorganisms, and highly pathogenic class 3 toxins.
Platform: CECEMA – Center for Experimental Animal Breeding and Conditioning
The CECEMA technical platform is a shared service of the University of Montpellier; it is part of the RAM (Montpellier Animal Facilities Network) and is designed to house animals needed for scientific research and teaching.
Platform affiliated with the Biology-Health Cluster: BNIF – BioNanoImaging Foundry
The BNIF technology platform at the University of Montpellier has state-of-the-art equipment that research teams in instrumentation, methodology, image processing, biology-health, and plant physiology use and continue to develop. The platform is formally attached to the MIPS department, but by its very nature, it interacts extensively with the other Biology-Health, Agronomy, and Chemistry clusters, which are the main users of the tools.
Pricing
Long-Term Thematic Projects
PTL COSMIC – Complex Organoid Systems with Multifaceted Interactions
- Responsible: Nathalie Chazal, IRIM
- Website
PTL HiLight – Intimate Exploration of Life: High Spatial and Temporal Resolution Analysis
- Manager: Julie Perroy, IGF
- Website
The I-SITE program of excellence, led by the University of Montpellier, has decided to provide strong support for research by creating Long-Term Thematic Projects (PTLs). The overall aim of these programs is to support research in Montpellier, to foster new scientific frontiers, and to support training through research. After consulting with our community and discussions organized by the Biology-Health Cluster, two PTLs in Biology-Health have emerged. The first concerns the development of new experimental models for the translational research of tomorrow (called COSMIC), while the second concerns high spatial and temporal resolution analysis of living organisms (called HiLight).





